
Rent of factory building, electricity, gas and coal used in production, salaries of production managers, depreciation of production machines and equipment are a few examples of these costs. Conversion cost is the cost incurred by any manufacturing entity in converting its raw material into finished goods capable of being sold in the market. It usually includes the total value of labor cost and other applied overheads like factory overheads, administrative overheads, etc. In some industries, conversion costs, including labour expenses, can exceed the total expenses on raw materials. In the food industry, converting raw food materials into edible food items is labour-intensive and requires specialised machinery.
Which Costs Are Both Prime and Conversion Costs?
Some common examples are insurance, building maintenance, machine breakup, and taxes on equipment or machining. The iron, aluminium, and SBR tyres expenses are considered raw material charges in the example. They invested conversion cost formula ₹2,00,000 in galvanised iron sheets, ₹1,50,00 in aluminium sheets, ₹80,000 on SBR tyres, and paid ₹1,00,000 as employee wages. Beginning inventory is used to calculate the average inventory for an accounting period.
- Rather, such expenses are considered as indirect labor which goes to the entity’s total manufacturing overhead cost (discussed later in this article).
- In this case, although the formula may seem simple compared to others that we can know in the economic field, determining costs that have some relation to the conversion process is a task that needs a good analysis.
- For example, if your conversion metric is signing up for your email list, the signup form should be prominent.
- Of course, that is not always possible, such as in the case of shorter advertising campaigns.
- Timber, glue, nails, glass and finishing materials have been treated as direct materials because they all become part of finished and ready to sell table.
10 Conversion Costs
The more complex and sophisticated the products become, though the higher this cost can potentially go up. The use of this ratio in process costing is to calculate the cost for both direct labor and manufacturing overheads. It’s important because it will become the cost of the inventory which will impact the selling price.
Omit ‘Indirect’ Costs
Thus, conversion costs are all manufacturing costs except for the cost of raw materials. Expressed another way, conversion costs are the manufacturing or production costs necessary to convert raw materials into products. However, a difference between prime costs and conversion costs that has not been incorporated in the analysis above is the fact that conversion costs also include indirect labor. The calculation for conversion costs includes direct labor in addition to overhead expenses. Like prime costs, conversion costs are used to gauge the efficiency of a production process, but conversion cost also takes into account overhead expenses that are left out of prime cost calculations. Direct labor costs include the salaries, wages, and benefits paid to employees who work on the finished products.
Unit Converter ▼
Beginning inventory refers to the total value of the inventory an organization holds at the start of an accounting period. Beginning inventory does not appear in the balance sheet as organizations prepare financial statements at the end of the accounting period. The value of ending inventory that appears in the balance sheet of the preceding year is carried forward as the beginning inventory for the current year. Conversion costs are vital to be calculated by each companysince they are fundamental for making important business decisions and carryingout basic accounting tasks. Prime costs are reviewed by operations managers to ensure that the company is maintaining an efficient production process.

- Hence, using conversion costs is an efficient way of calculating equivalent units and per unit costs rather than separately calculating direct labor and manufacturing overheads.
- They offer insights into the efficiency of manufacturing operations and potential areas for cost reduction.
- Operations managers use conversion costs to help identify waste within the manufacturing process.
- Conversion costs is a term used in cost accounting that represents the combination of direct labor costs and manufacturing overhead costs.
- Prime Cost, however, is the sum of direct materials and direct labor, focusing specifically on fundamental production costs.
For this reason, it’s a more relevant number for operations managers, who may be looking at ways to reduce the indirect expenses of production. Prime costs and conversion costs include some of the same factors of production expenses, but each provides a different perspective when it comes to evaluating production efficiency. Assume that direct materials cost $700, direct labor is $500, and factory overhead is $300 for cabinets that have been manufactured. For example, the value of depreciation of the machinery in a particular accounting period falls under the category of manufacturing overheads.
Unit Converter ▲
The total of the cost per unit for material ($1.17) and for conversion costs ($2.80) is the total cost of each unit transferred to the finishing department ($3.97). Therefore, one difference https://www.bookstime.com/ between the two concepts is that manufacturing overhead is only included in conversion costs. The other difference is that the cost of direct materials is only included in prime costs.
In other words, conversion costs are a manufacturer’s product or production costs other than the cost of a product’s direct materials. It helps businesses understand the expenses involved in converting raw materials into finished products. This guide will explain what conversion cost is, how it is calculated, and provide an example to make it easy to understand. The calculation for prime costs includes the amounts spent on direct materials and direct labor.
- Conversion costs only include direct labor and manufacturing overheads because of the reason that these two variables are rudimentary to execute the overall process.
- Therefore, once the batch of sticks gets to the second process—the packaging department—it already has costs attached to it.
- This report shows the costs used in the preparation of a product, including the cost per unit for materials and conversion costs, and the amount of work in process and finished goods inventory.
- Each has its own example of how you would assess conversions with your given definition for the conversions.
- This knowledge helps companies make informed decisions and enhances their ability to succeed in the marketplace.
- One can arrive at total period costs by closely monitoring and reporting the expenses that aren’t related to manufacturing a product.
How to Calculate Beginning Inventory & Conversion Costs
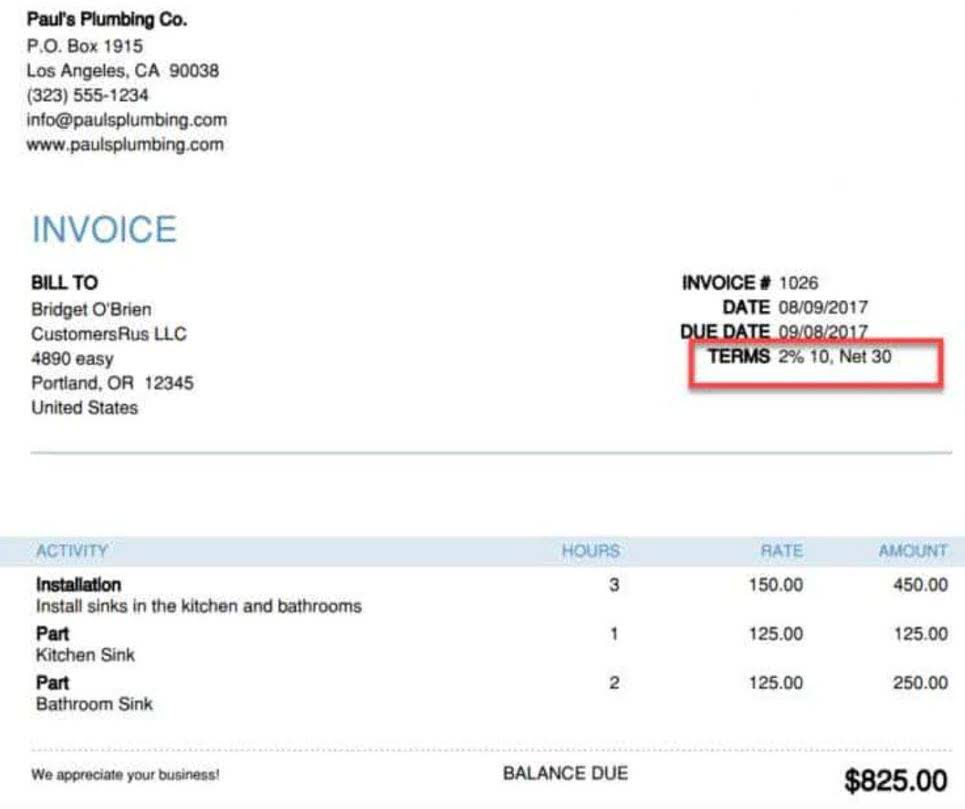
During June, Excite Company’s prime cost was $325,000 and conversion cost was $300,000. Operations managers use conversion costs to help identify waste within the manufacturing process. Overhead costs are expenses that cannot be directly attributed to the production process but are necessary for operations, such as the electricity required to keep a manufacturing plant functioning throughout the day. The furniture maker charges $50 per hour for labor, and the project takes three hours to complete. As reported in Corporate Finance Institute, period costs are the expenses that aren’t incurred by manufacturing a product. The examples of period costs are legal costs, promotion costs, administrative costs and sale commissions.